![]() What material is best suited as thermal insulation, fixtures, and setters in furnaces with hydrogen atmospheres? To find out, ZIRCAR Ceramics, Inc. reports on a series of test results that determine the weight loss and shrinkage of six materials you may use in your heat treat furnace.
What material is best suited as thermal insulation, fixtures, and setters in furnaces with hydrogen atmospheres? To find out, ZIRCAR Ceramics, Inc. reports on a series of test results that determine the weight loss and shrinkage of six materials you may use in your heat treat furnace.
Multiple types of fibrous alumina insulation materials were tested to determine their stability in hydrogen gas. Silica bonded types have been known to give superior performance in oxidizing and neutral environments. Alumina bonded types have classically been used as thermal insulation, fixtures and setters in applications where reduction by aggressive furnace atmospheres is encountered. One such aggressive reducing atmosphere is hydrogen, a common cover gas in furnaces for sintering powder metal parts. In hydrogen gas atmospheres, silica -- a common binder which imparts high temperature stability and increased mechanical strength -- is attacked, dissociates and volatilizes resulting in premature failure of the refractory.
Test Method
Cubes of insulation, roughly 1 inch per side, were measured and weighed. They were fired at 1450°C in a model 1725 HTF box furnace manufactured by CM Furnaces, Inc. The furnace was purged with 15 scfh hydrogen gas with a dew point of <40°C. It was heated at a rate of 200°C per hour with soak times of 1, 2, 10 and 50 hours. The samples were removed after each soak, measured and weighed. Weight loss and thickness shrinkage were calculated using experimental data. Shrinkage in the length and width directions were averaged to obtain the data displayed. The materials tested are described in the following table.
Results
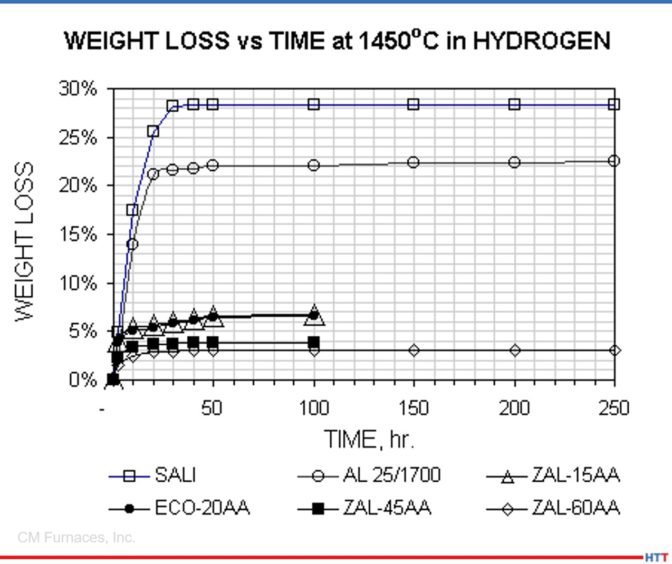
Weight Loss results for all types tested.
Weight Loss results for alumina bonded types tested. Shrinkage results in length and width directions for all types tested.
Shrinkage results in length and width directions for all types tested.
Shrinkage results in thickness directions for all types tested.
Conclusions
Premium (ZAL-45AA) and special (ZAL-60AA) grade fibrous alumina insulation materials appear best suited for use as thermal insulation, fixtures, and setters in furnaces with hydrogen atmospheres as they exhibited the least weight loss and thermal shrinkage of all specimens tested.
Alumina bonded materials (ZAL-15AA, ECO-20AA, ZAL-45AA and ZAL-60AA) showed significantly less weight loss after exposure to hydrogen gas at 1450°C than did the silica bonded types tested.
Silica bonded materials (SALI and AL 25/1700) exhibited significant weight loss after testing at 1450°C in hydrogen.
Thermal shrinkage is inversely proportional to density, independent of the bond type.
Acknowledgements
The data presented in this article was collected by CM Furnaces, Inc. (www.cmfurnaces.com) and provided to ZIRCAR Ceramics, Inc. by Donald T. Whychell Sr., director of Research and Development at CM Furnaces, Inc. (dwhychell@cmfurnaces.com)
.
Search suppliers of ceramic parts and fixtures on Heat Treat Buyers Guide.com