What are advanced management systems and how does deep integrative system management software help automotive heat treaters improve processes while saving on time and unnecessary expenses? Explore the future of software technology for the management of heat treating operations in this Technical Tuesday by Sefi Grossman, founder and CEO of CombustionOS.
This informative piece was first released in Heat Treat Today’s August 2024 Automotive print edition.
The heat treating industry is on the brink of a technological transformation. Just as the momentous adoption of websites and emails transformed the nature of work for manufacturers, the advanced software systems are thrusting us into a new era of simplicity, automation, and deep integrations.
This article explores how advanced systems — an application of ERP (enterprise resource planning) and MES (manufacturing execution systems) combined with the power of AI — is revolutionizing facility operations, enhancing quality, efficiency, and profitability.
What Are Advanced Systems?
Advanced systems simplify, streamline, and automate operations by lifting the data burden off of plant personnel. While most existing systems focus on the part inventory workflow, more advanced systems go beyond by directly integrating into the heat treat process to track at bin/tray/tree level.
This requires real-time scheduling control, barcode scanning, digitizing recipe and process (no more paper), and direct sensor/PLC integration. Because of its critical nature, an advanced system is most likely an on-premise and cloud “hybrid solution” that is not crippled by internet connectivity issues. This allows it to still utilize rapidly evolving cloud systems that provide external services like messaging, big data storage, and AI to name a few.
Precise Processing
Repeatable, accurate methods to ensure optimal time, temperature, and atmosphere of the decided heat treatment processes are possible with advanced systems.
Utilizing existing sensors and hardware interfaces, data is collected in short intervals, transformed into meaningful data formats, and stored in a database. Network technologies such as HTTP, Modbus, and other analog to AI technologies make this possible with minimum additional hardware. The data is managed locally on the facility network, and synchronized with cloud services for further processing, analysis, and long-term history storage.
With a close monitoring of all these variables, facilities can tighten acceptable specification ranges. Deep integration with equipment ensures that data flows seamlessly from sensors and devices to the central system.
This real-time data collection and processing enables facilities to monitor operations continuously and make informed decisions quickly. For example, integrating data from temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and other monitoring devices ensures that all critical parameters are tracked and managed effectively. Additionally, if a temperature reading deviates from the acceptable range, the system can immediately alert the relevant personnel, allowing them to take corrective action before it becomes a critical issue.
In addition to quality assurance, integrated artificial intelligence tools optimize job scheduling. Unlike traditional date/time calendar methods, AI systems predict job completion times based on real-time process data. This is particularly useful for roller furnace setups, where continuous processing occurs, but it is also beneficial for batch furnaces. Optimized scheduling improves resource allocation and operational efficiency, ensuring that jobs are completed on time and to the required specifications. The difference between a “calculation algorithm” and AI is that, with AI, you do not have to pre-program it. It automatically learns and adjusts for known variability in your hardware and even the personnel that are operating the equipment.
Finally, the automation of these systems captures and records all necessary information accurately. This reduces the risk of non-compliance, improving the overall quality of the final product. For example, a Detroit-based heat treating facility reported that accessing real time data to ensure compliance with industry standards has allowed them to spend 40% less time on documentation tasks.

Alleviating Burden on Maintenance and Inventory
Predictive maintenance is one of the most significant applications of AI in the heat treating industry. Traditional maintenance schedules are often based on fixed intervals, which can lead to unnecessary downtime or unexpected failures. AI driven predictive maintenance, on the other hand, uses real-time data to determine the optimal times for maintenance activities. This approach not only reduces downtime but also extends the lifespan of equipment.
A Detroit-based heat treating facility implemented an AI-driven predictive maintenance system (PMs) and saw a 25% reduction in equipment downtime. By analyzing data from critical parts, inventory, process tracking history, and various sensors, the AI system could predict when components were likely to fail, allowing the maintenance team to inspect and address issues proactively beyond their standard PMs. This not only improved operational efficiency, but also saved significant costs associated with emergency repairs and unplanned downtime.
Additionally, the integration of QR codes for inventory and process tracking enables quick and accurate data entry compared to manual logging. For instance, when racking parts out of bins, operators can simply scan QR codes, which automatically update the system with the relevant information. This not only speeds up the process but also minimizes the chances of human error.
Reducing Operational Costs
The adoption of advanced ERP and MES systems has led to substantial cost savings for many facilities. These systems reduce operational costs through the implicit automated integrations that technologies like CombustionOS bring. Here are just a few ways that operational costs have been cut:
- Decreasing shipping and receiving management from three to just one employee
- Minimizing rework costs by timely process alerts
- Reducing personnel by replacing constant manual oversight with accurate, digital tracking systems
- Lowering administrative costs by utilizing a more efficient and accurate invoice automation platform
Case Study: A client reported comprehensive cost savings, including a 20% reduction in shipping and receiving time, fewer logistics and furnace operators needed, a 33% decrease in rework costs, a 15% savings in maintenance costs, and a 25% reduction in accounting overhead. These efficiencies translate into substantial payroll savings and improved profitability.
How To Implement
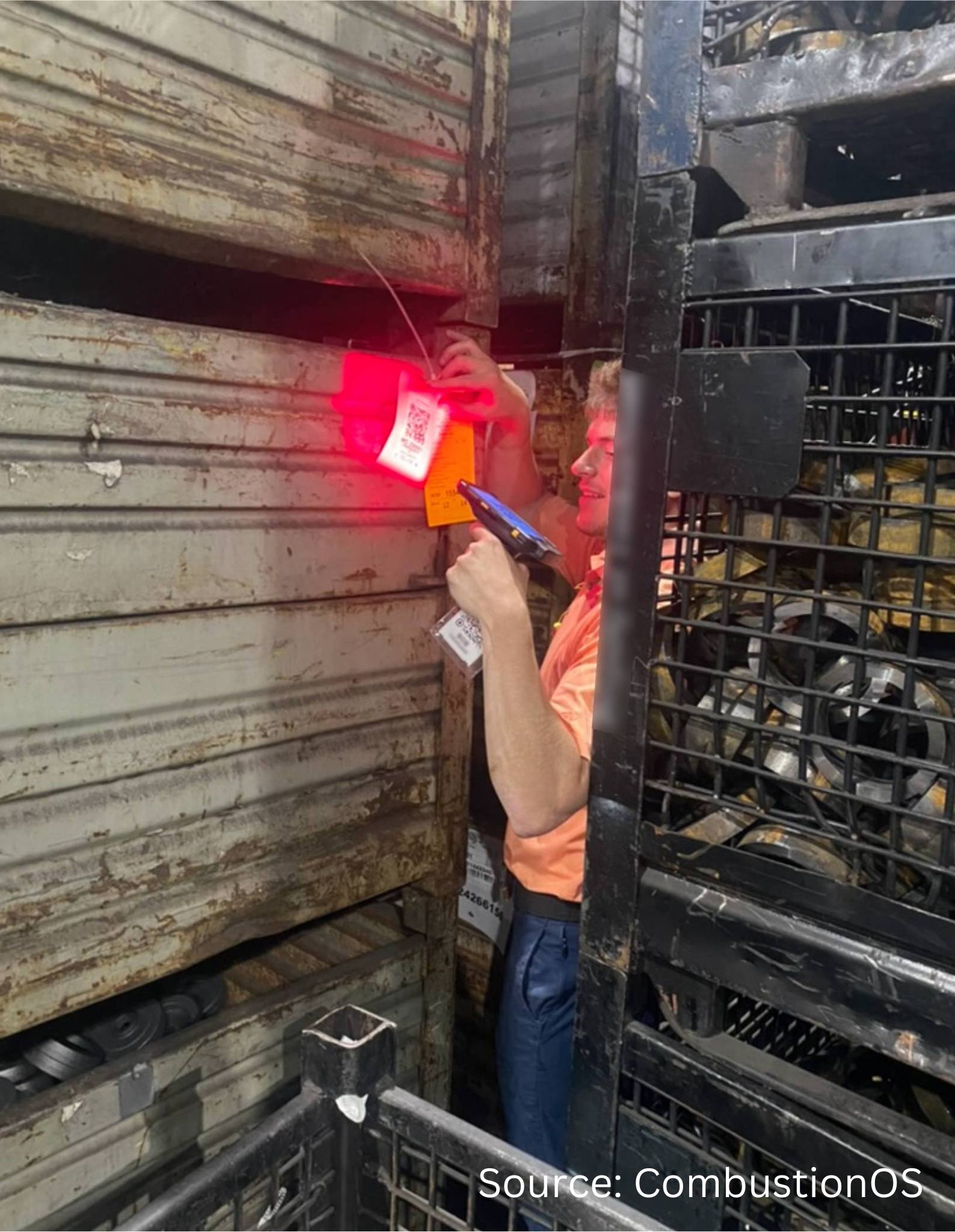

One of the most significant advancements in heat treating technology is the deep integration with various equipment types. Unlike traditional ERP systems, which often lack true integration, advanced systems work backwards from equipment data, building ERP functionalities around this integration to ensure seamless and accurate data flow.
First, there are advanced systems that can handle data from both digital and analog sensors. So, for heat treaters who are juggling a variety of sensors and systems, looking for an integrative advanced system that has adaptability will ensure compatibility with existing equipment while keeping an eye on cost. Facilities can continue using their current equipment while benefiting from advanced monitoring and control capabilities.
Second, advanced ERP/MES systems can take collaboration with multiple vendors. Rather than uproot current systems and relationships, work with an advanced systems provider who is able to collaborate with other software and systems. Advanced ERP/MES systems provide comprehensive solutions that include deep equipment integration and full ERP functionalities. This approach reduces the complexity and cost of integration, ensuring that all components work together seamlessly.
Key Applications
Most operations in a heat treat department will benefit from advanced systems due to the time-saving automations that the system integrates. But many heat treaters are looking to adapt and integrate older systems and often more complex designs, like roller hearth furnaces. Here are some steps that experts will take to guide you through to make the digital integration smooth and effective:
- First, it is important to understand you don’t need to boil the ocean. Starting with a more advanced inventory tracking system that employs barcodes can set the underpinnings for a more integrated system while providing immediate benefits to your logistics.
- Then, it is also key to get a deep understanding of your current process and map out your operational workflow. Using a flowchart program helps
visualize the process to make sure all stakeholders are on the same page. - Some aspects of your current process are probably outdated (perhaps created by someone who is no longer at the company), while others are key to the core of how you operate. Understanding the difference is crucial to make sure you unlock potential automation without disturbing your core process and flow.
- You’ll then need to prepare every required form, document, chart etc. that you use in the operation. For process control, recipes, and lab testing, provide many parts/iterations to capture the complexity.
- Finally, take inventory of any existing digital systems you have adopted, like inventory tracking, spreadsheets, or custom software. The existing system
network, including servers, Wi-Fi setup, and hardware (PCs, printers, scanners, etc.) will be utilized as much as possible in the transition to reduce the need to purchase and set up different equipment.
Conclusion
The future will require constant innovations and thoughtful leveraging of increasingly advanced systems. Unlike static, homegrown, or “pieced together” solutions, the most advanced systems are constantly updated with new features, ensuring they remain at the cutting edge of technology. Engaging directly with plant personnel to understand their needs and challenges allows systems like CombustionOS to evolve and improve continuously.
The heat treating industry is on the cusp of a technological transformation, driven by advancements in ERP, MES, and AI. These technologies offer the potential to enhance quality, efficiency, and profitability, making them essential for the future of manufacturing. By embracing automation, integrating advanced AI capabilities, and committing to continuous innovation, the industry can achieve new levels of operational excellence.
About the Author:

Founder & CEO
CombustionOS
Source: Author
Sefi Grossman has been at the forefront of technology revolutions for the past two decades and has been leading the technology company CombustionOS for nearly seven years.
For more information: Contact Sefi at sefi@combustionos.com.






