Like most power systems, power control dates back to vacuum tube technology. Like radios, amplifiers, and other industrial equipment, the furnace market started using transistors as the technology evolved. Vacuum tubes were not generally balanced and contained poisonous elements and were phased out of usage in almost all industries. In this Technical Tuesday installment, guest columnist Stanley Rutkowski III, senior applications engineer at RoMan Manufacturing, Inc., distinguishes the different methods used to regulate power input to furnaces.
This informative piece was first released in Heat Treat Today’s August 2024 Automotive print edition.

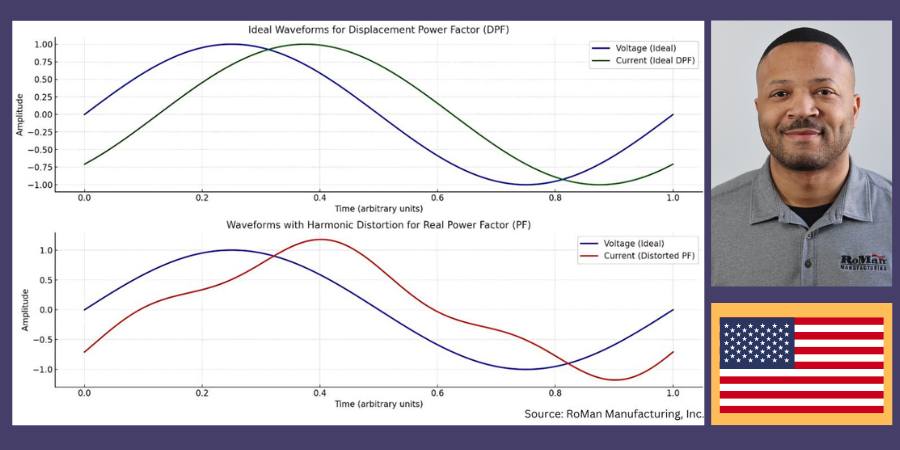
Source: RoMan Manufacturing, Inc.
In today’s furnace market, there are generally three primary types of control systems: VRT, SCR, and IGBT. Each of these control technologies employs different methods to regulate the power input to the furnace, which in turn generates the required heat. These control systems transfer the power from the plant power system to a transformer in line with the load (heating elements). Power is delivered to a plant in a three-phase system from the utility company. The least costly and highest power factor systems have a balanced load across the three phases during the operation of any furnace.
VRT (Variable Reactance Transformer)
A VRT incorporates a feedback mechanism to either increase or decrease the amount of DC injected into the controlling reactor in the system. This increases or decreases the amount of current in the system to control the heat in the furnace by comparing it to the scheduled setpoint. A VRT system can have the following configurations:
- Single-phase power controller for single load applications
- Scott-T three-phase power controller (this is a system that allows all three phases of the incoming power system to be utilized in a two-phase load application)
- Three-phase power controller (in either a Delta or Wye configuration) for three zone load applications
SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier)
An SCR control system uses a pair of thyristors (gated diodes) to control the amount of power applied to the primary of a transformer. The SCR control delays the start of the waveform, and the control point is reset when the waveform crosses the zero line. An SCR system can have the following configurations:
- Single-phase, phase-angle controlled for single load applications
- Single-phase, zero-cross controlled for single load applications
- Single-phase, on-load, tap-changing controlled (this incorporates multiple pairs of the thyristors together to lessen the losses of the SCR system)
- Scott-T three-phase power controlled (this is a system that allows all three phases of the incoming power system to be utilized in a two-phase load application)
- Three-phase, phase-angle controlled (in either a Delta or Wye configuration) for three zone load applications
- Three-phase, zero-cross controlled (in either a Delta or Wye configuration) for three zone load applications
IGBT (Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor)

Source: RoMan Manufacturing, Inc.
An IGBT uses a diode bridge, capacitor, and switching transistors to control the amount of power applied to the primary of a transformer. The input frequency to the transformer is controlled by the switching transistors. The diode bridge is connected to the three-phase system allowing single, Scott-T (two zone), or three zone systems all to pull a balanced load across the three phases of the plant power system. A line reactor is incorporated to maximize the power factor in the system, minimizing the total power usage of the furnace. The IGBT system also uses a square wave into the transformer and a rectifier after the transformer to remove inductance out of the power delivery system to reduce costs of cables, breakers, and other components in the total package.
About the Author:

Senior Applications Engineer
RoMan Manufacturing, Inc.
Stanley F. Rutkowski III is the senior applications engineer at RoMan Manufacturing, Inc., working on electrical energy savings in resistance heating applications. Stanley has worked at the company for 33 years with experience in welding, glass and furnace industries from R&D, design, and application standpoints. For more than 15 years, his focus has been on energy savings applications in industrial heating applications.
For more information: Contact Stanley at srutkowski@romanmfg.com.