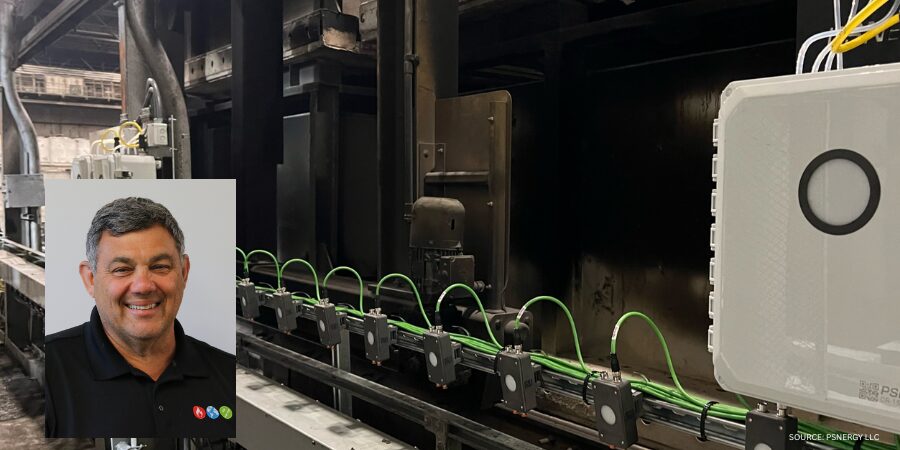
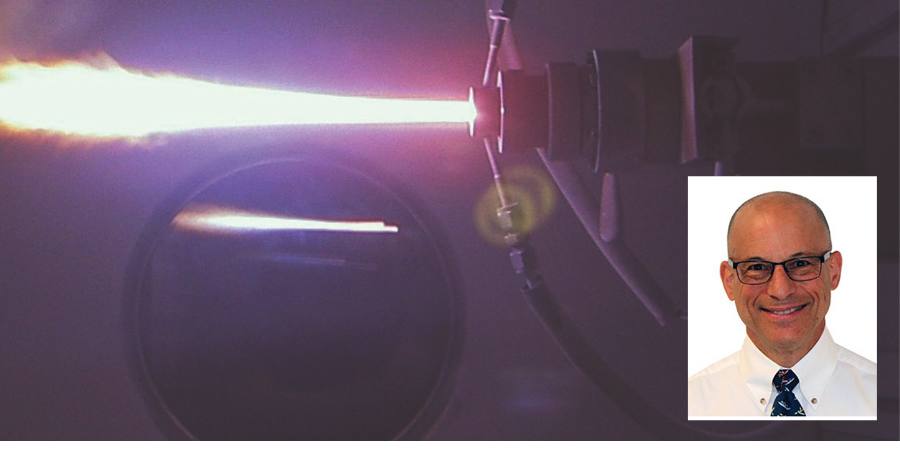
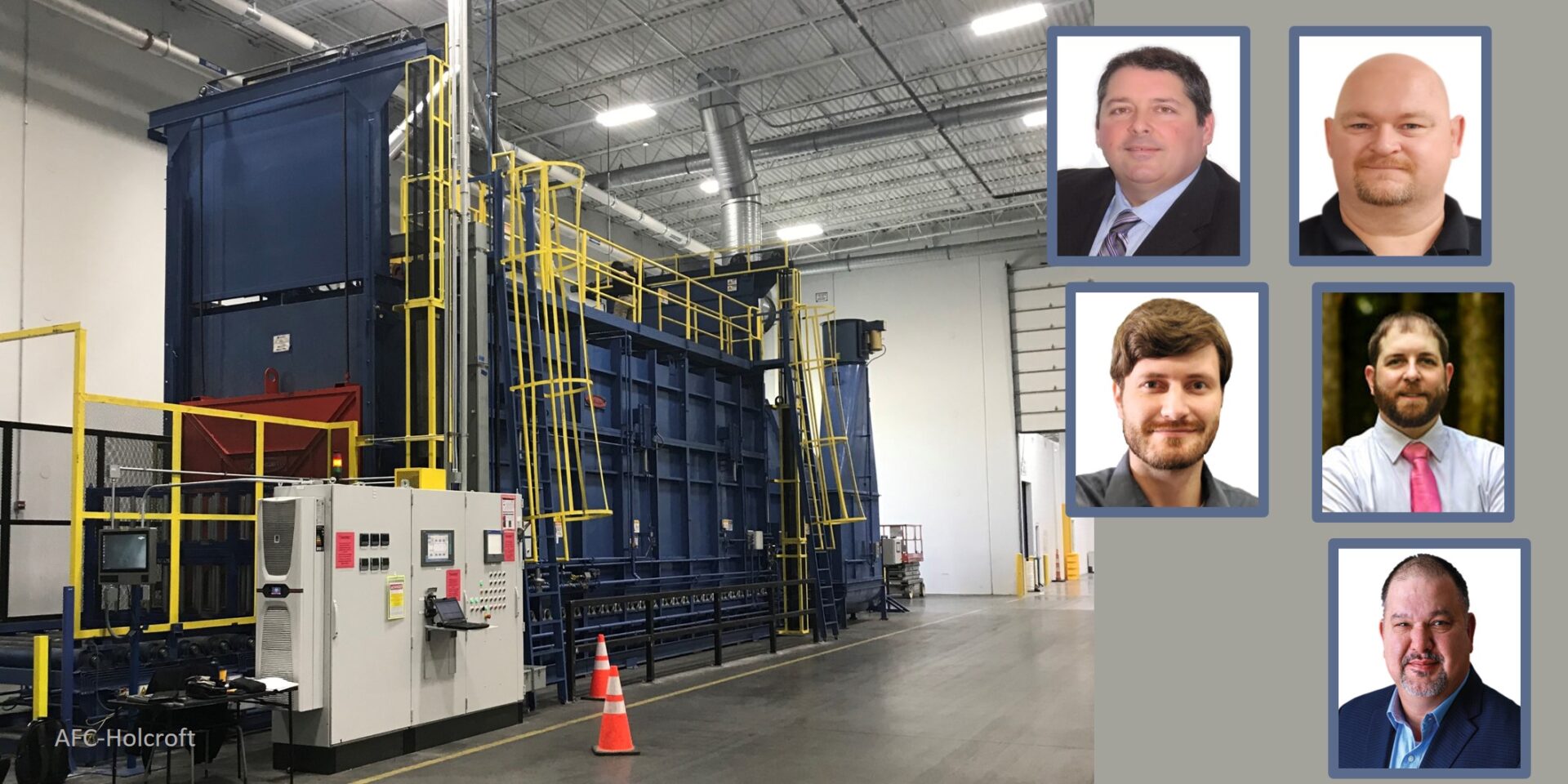
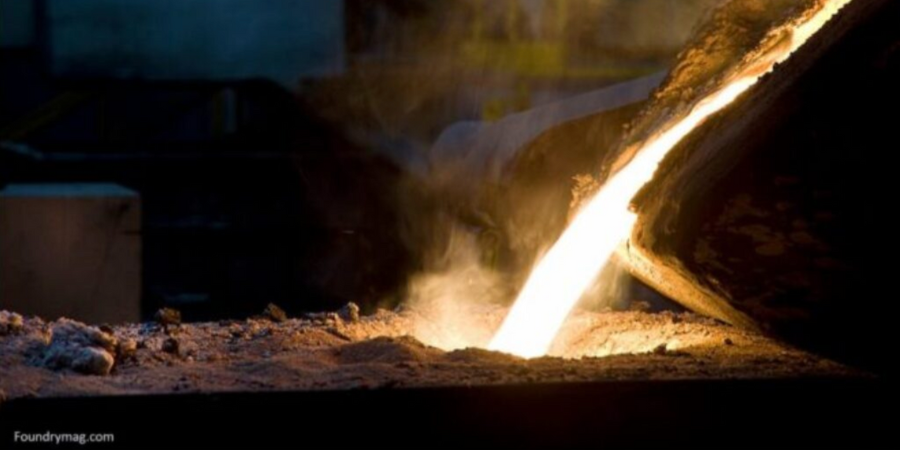
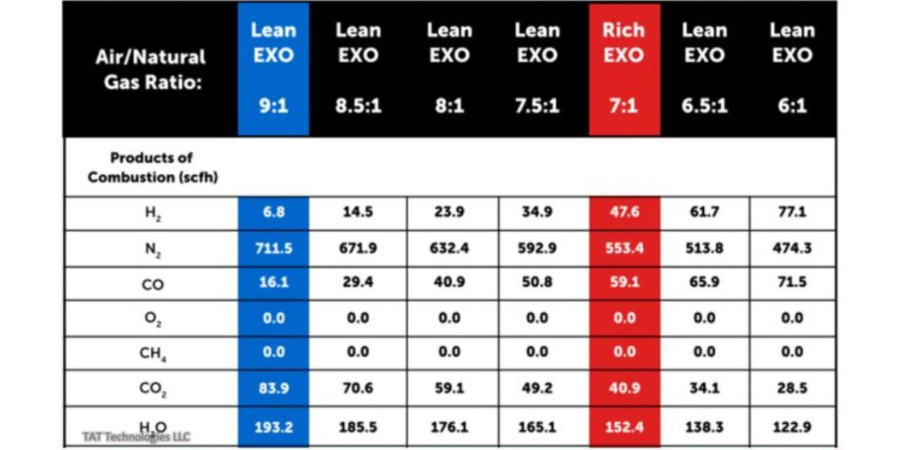
Annealing
Used for a variety of reasons — grain refinement, microstructural property changes and enhanced ductility to name a few — annealing is most frequently used to soften a part to improve its machinability. Annealing involves heating metal to a specified temperature (depending on the type of annealing being performed), holding the metal at that temperature for a suitable amount of time, reducing the temperature in a controlled ramp rate (if applicable), soaking at a lower temperature, and slow furnace cooling. Annealing is used across the heat treat industry and can be performed on a variety of materials. It is most commonly used in treating steel and cast iron. It is often performed at the steel mill prior to shipment of the material to the distributors or end users.