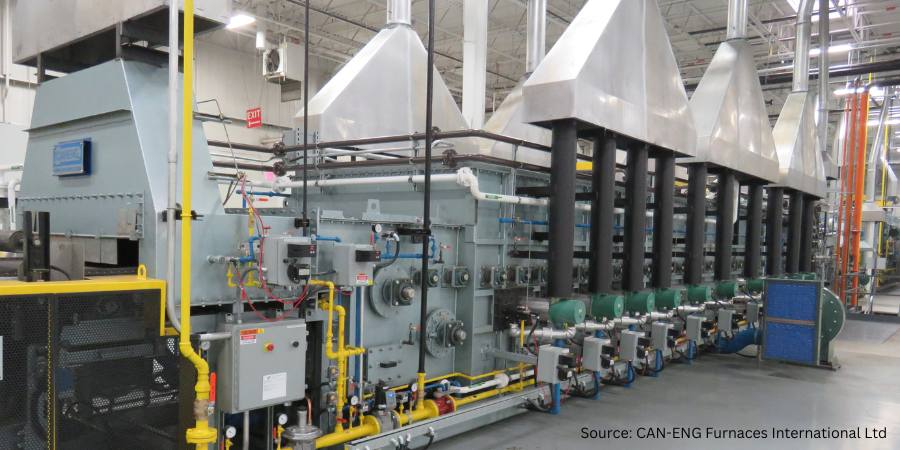
Quenching
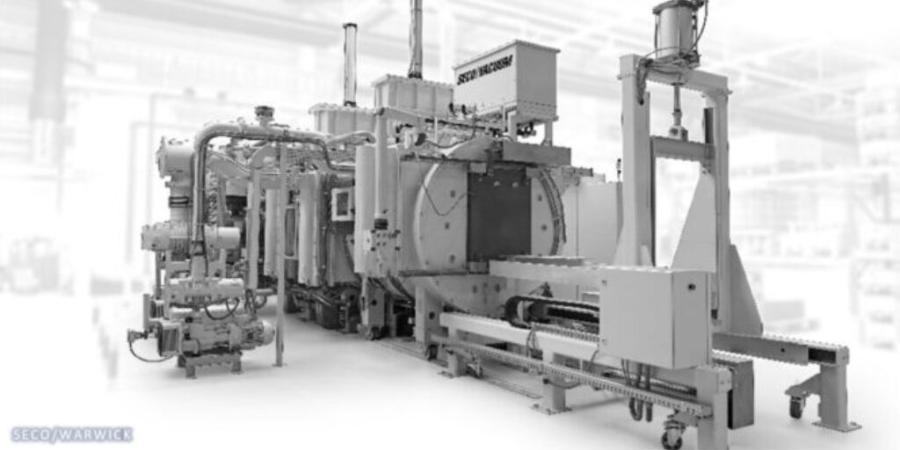
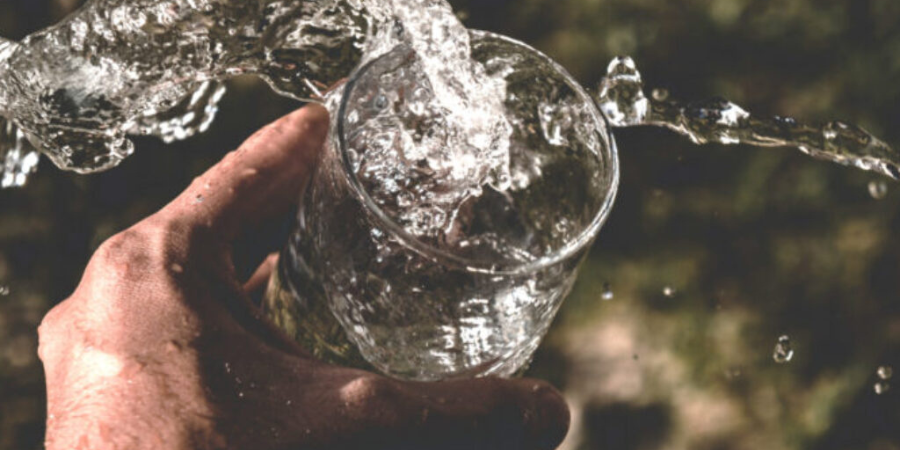
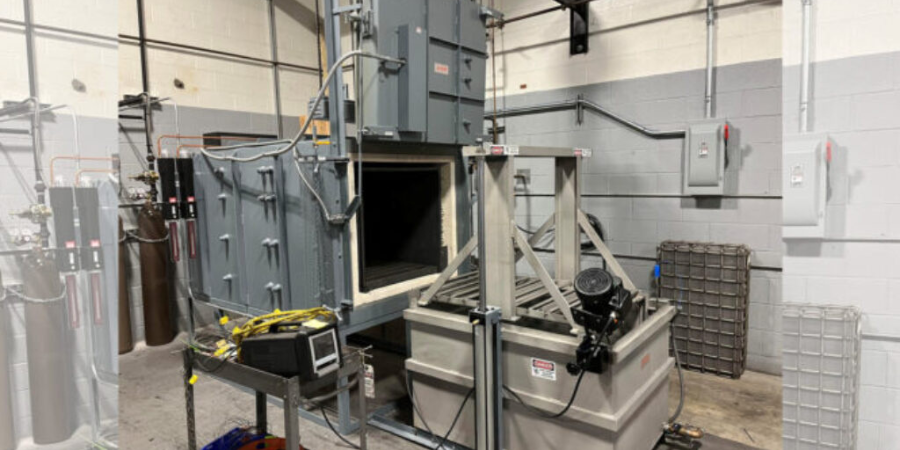
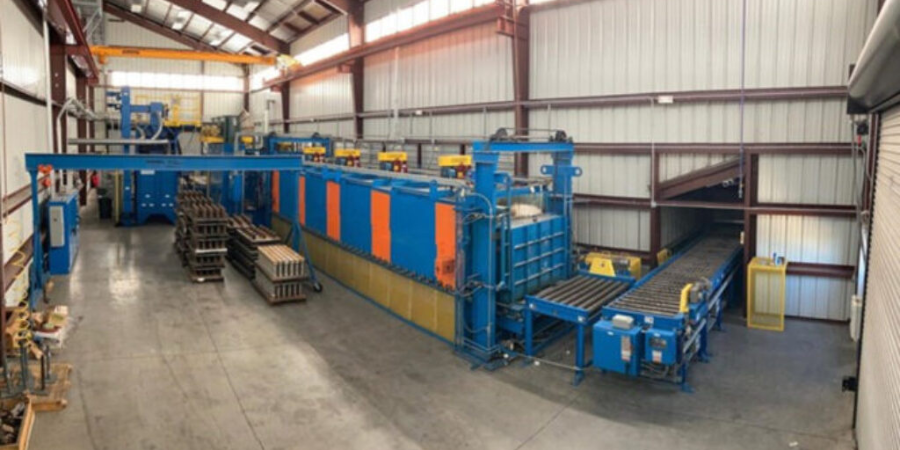
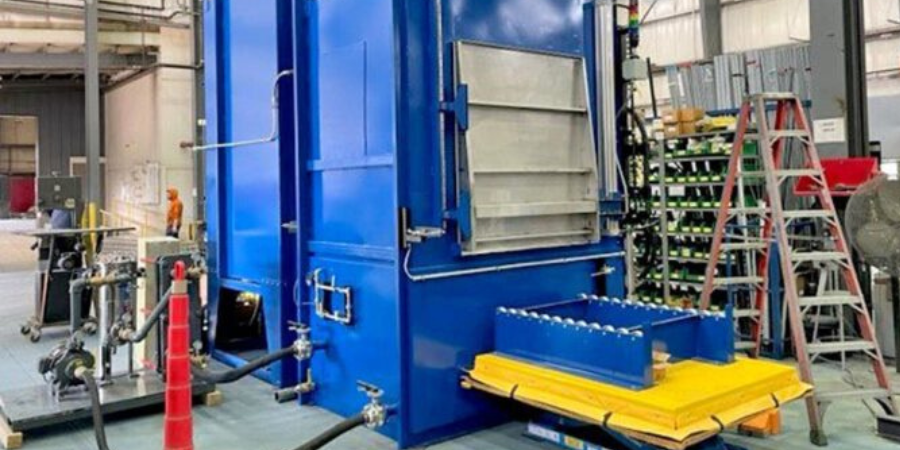
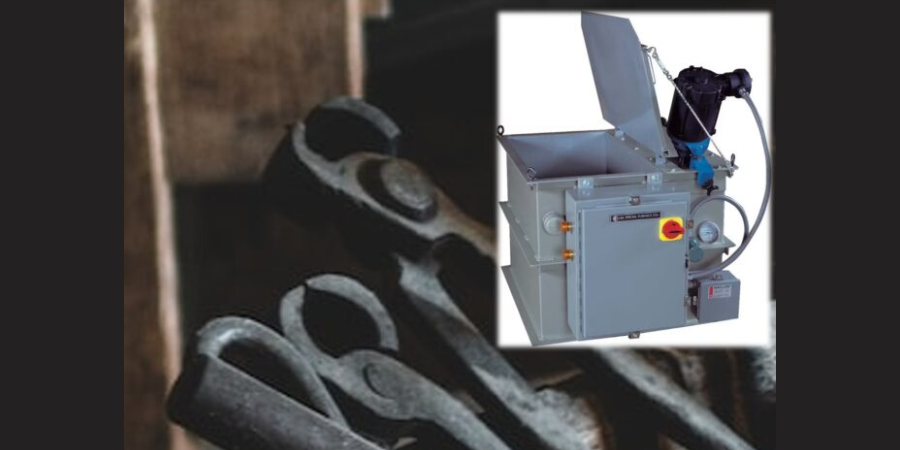
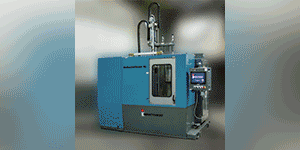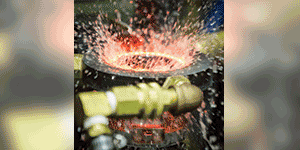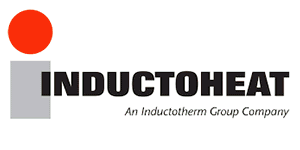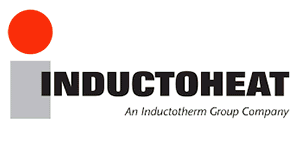
Quenching is a critical step in virtually all heat treating processes. It is usually performed after the holding at austenitizing temperature (for hardening or case hardening operations). The purpose of quenching is to (rapidly) cool the parts to achieve desired properties, microstructure, and dimensional tolerances. Quenching is widely performed on different types of metals using different media, such as brine or caustic, water, polymer, oil, high pressure gas (e.g., nitrogen, argon, helium, hydrogen), molten salt, air (still or moving), and cooling inside the furnace itself. Types of quenching include: direct quenching, interrupted quenching, selective quenching (typically used in induction hardening processes), and spray or fog quenching (typically used to accelerate air cooling).