As heat treaters strive for a sustainable future, pressure mounts to make the right choices while running commercially viable operations. This guest column by Michael Mouilleseaux, general manager at Erie Steel, Ltd., explores how and why heat treat operations are now coming under the focus of the U.S. Department of Energy.
This informative piece was first released in Heat Treat Today’s March 2024 Aerospace print edition.
The iron and steel industry contributes approximately 2.1% of energy-related CO2 emissions from primary sectors in the U.S. These statistics may seem insignificant or far removed, but the federal government has now determined that heat treating is a significant contributor and has set in motion critical changes for U.S. heat treaters.
Background

On December 8, 2021, President Joe Biden issued an executive order that committed the federal government to “lead by example” in U.S. efforts towards carbon-free and net zero emissions solutions. Since then, the executive has delegated the Department of Energy (DOE) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to spearhead these initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions (GHGE) and promoting energy efficiency across various sectors of the U.S. economy. To support these efforts, $10,000,000,000 in incentives are being allocated for the DOE and EPA to investigate and promulgate regulations.
Specifically, the government sees the “industrial sector” as responsible for close to a quarter of all greenhouse gas emissions (GHGE); the five industries named within this sector are chemical processing, petroleum processing, iron & steel production, cement production, and food & beverage manufacturing. The DOE is leading the efforts of “supercharging industrial decarbonization innovation” and leveraging the potential of “clean hydrogen.”
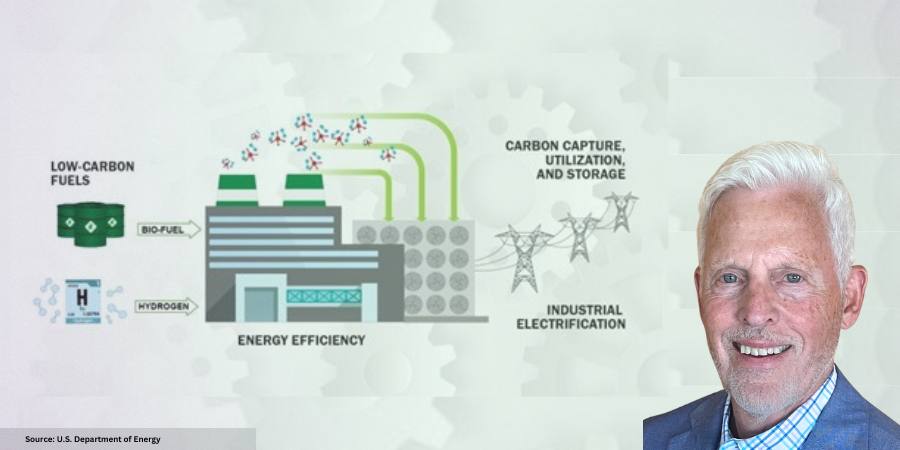
Following these directives, the DOE unveiled the “Industrial Decarbonization Roadmap” in September 2022. This strategic plan will guide decarbonization efforts of the five key industrial sectors to mitigate GHGE. The four pillars are:
- Energy efficiency
- Industrial electrification (using green electricity)
- Adoption of low-carbon fuels, feedstocks, and energy sources (LCFFES)
- Carbon capture, utilization, and storage at the generated source (CCUS)
The DOE determined that process heating — accounting for 63% of energy usage within the iron and steel industry — would be the best opportunity to apply these four pillars. However, until May 2023, heat treating had not been explicitly mentioned as a target for decarbonization efforts.
Why Should Heat Treaters Care?
In May 2023, the Industrial Efficiency & Decarbonization Office — an office within the DOE’s Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy — held a symposium to refine its commitment to the decarbonization of the industrial sector. It was then that heat treating was specifically defined as a process targeted for the reduction of GHGE in the steel, aluminum, and glass manufacturing industries.
The DOE’s refined commitment focuses on two things: reduce GHGE attributable to “process heating” by 85% by 2035 and achieve net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050. To reach these ambitious goals, the DOE emphasized the importance of adopting LCFFES, green electrification, and implementing strategies that promote industrial flexibility, advanced heat management, smart manufacturing, and alternative technologies.
The potential ramifications of the DOE’s efforts on the heat treating industry are momentous. With the development of regulations to support these efforts, businesses within this sector must prepare for significant changes. The focus on green hydrogen, biofuels, and electrification, coupled with advanced technological solutions like ultra-efficient heat exchangers, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and alternative no-heat technologies, are strategies being considered for potential regulation.
Conclusion
The heat treating industry stands at a crossroads, with the DOE’s decarbonization initiatives signaling a shift to adopt cleaner energy practices. As these regulations take shape, businesses will need to adapt, investing in new technologies and processes that align with the nation’s clean energy goals. In the next column, we’ll address potential ramifications of the DOE effort for industrial decarbonization in the heat treating industry to help you be better informed and prepared.
About the Author:

General Manager at Erie Steel, Ltd.
Michael Mouilleseaux is general manager at Erie Steel, Ltd. He has been at Erie Steel in Toledo, OH since 2006 with previous metallurgical experience at New Process Gear in Syracuse, NY, and as the director of Technology in Marketing at FPM Heat Treating LLC in Elk Grove, IL. Michael attended the stakeholder meetings at the May 2023 symposium hosted by the U.S. DOE’s Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. He will be speaking on the MTI podcast about this subject on March 5, 2024, 2:30 EST, and will present on this topic at the April 3, 2024, MTI Mid-West chapter meeting.
For more information: Contact Michael at mmouilleseaux@erie.com.