![]() Source: Materials Today
Source: Materials Today
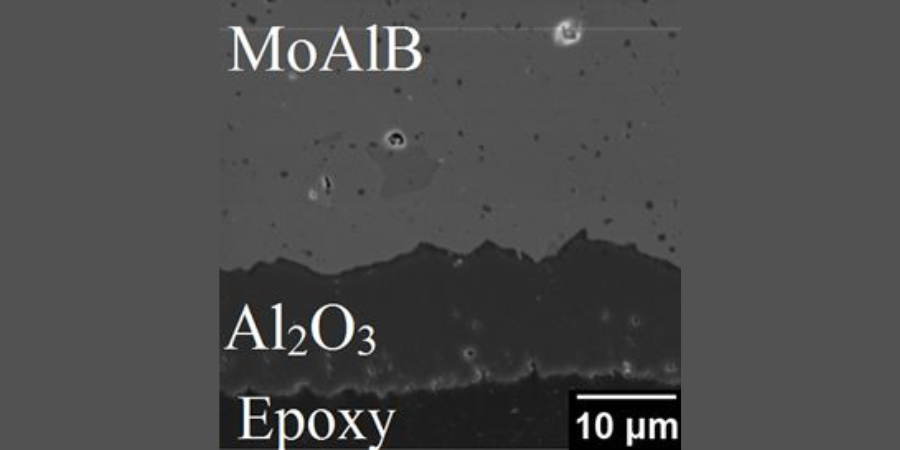
“This resistance to oxidation is possible because of the presence of aluminum in layers between molybdenum and boron layers,” Barsoum said. “When heated to high temperatures in air the aluminum atoms selectively diffuse to the surface and react with oxygen – forming a surface aluminum oxide, or alumina, protective layer that slows down further oxidation considerably. So the material forms its own protective coating.”